Sets
While the developer documentation on $sets and the +in core is comprehensive, it is organized alphabetically which can make it difficult to see what's going on with set relations. This article will describe set identities and relations through the Hoon standard library.
A $set is a tree with a particular internal order based on the hash of the value. This tends to balance the values and make lookup and access more efficient over large sets.
Set Creation & Membership
Define a Set
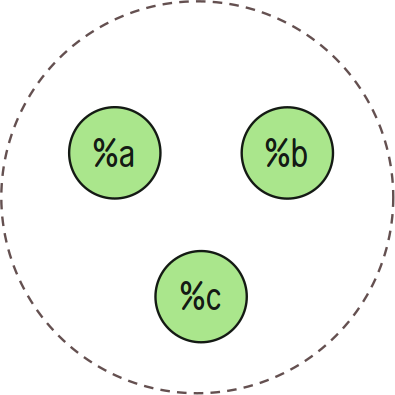
+silt produces a $set from a $list.
Add Members
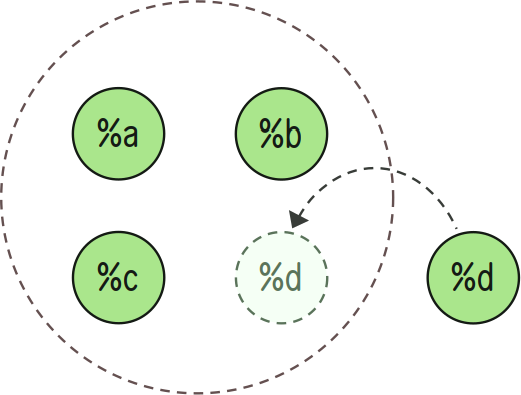
+put:in adds an element x to a set A.
+gas:in adds each element x, y, z of a list to a set A.
Remove Members
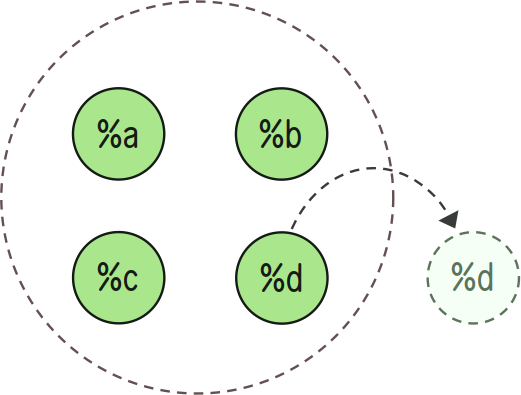
+del:in removes an element x from a set A.
Membership
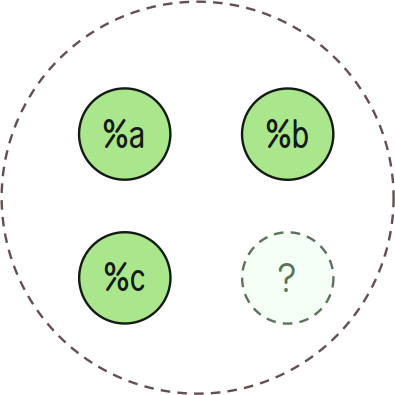
+has:in checks if an element x is in a set A.
Size
+wyt:in produces the number of elements in A as an atom (width).
Export as List
+tap:in produces the elements of set A as a $list. The order is the same as a depth-first search of the $set's representation as a $tree, reversed.
Set Relations
First we consider the elementary operations between two sets.
Union (A ∪ B)
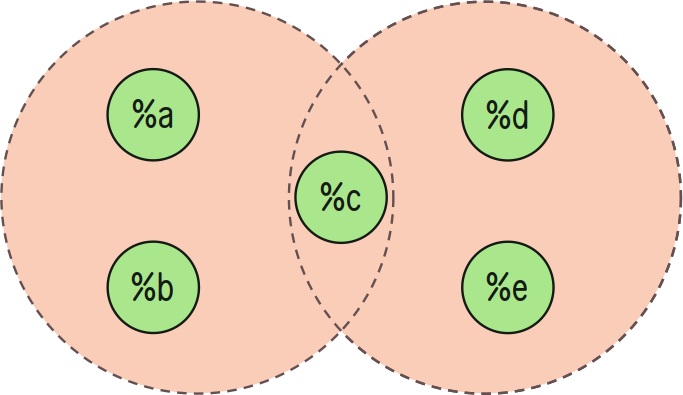
+uni:in produces a set containing all values from A or B. The types of A and B must match.
Intersection (A ∩ B)
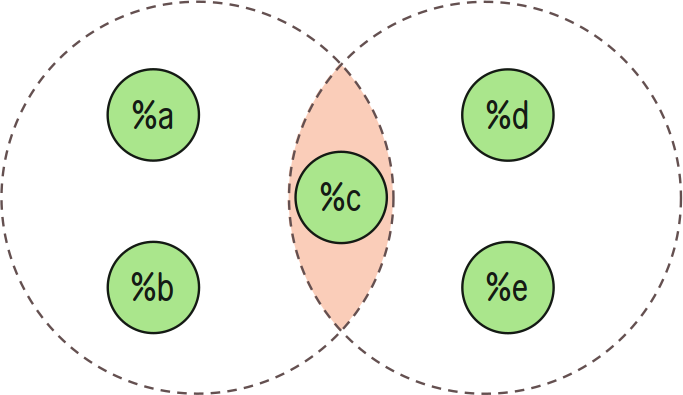
+int:in produces a set containing all values from A and B. The types of A and B must match.
If two sets are disjoint, then their intersection is ∅.
Complement (Aꟲ)
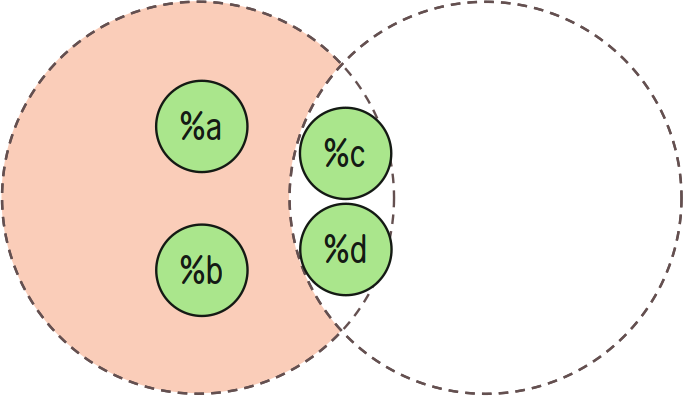
The complement of a set A, Aꟲ, may be found using +dif (difference).
For instance, if X = {a, b, c, d} and A = {c, d}, then Aꟲ = {a, b}.
Symmetric Difference (A Δ B)
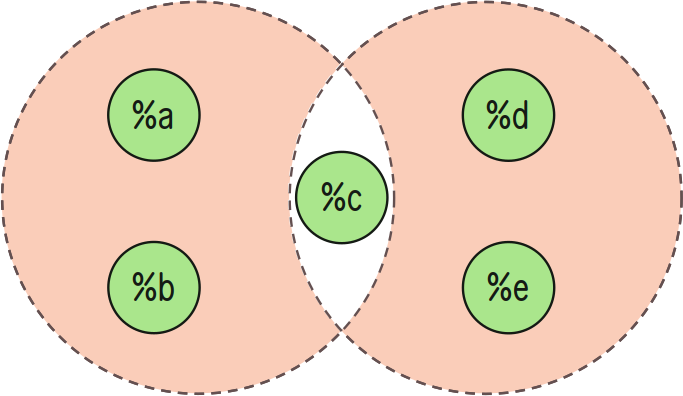
The symmetric difference of two sets A and B consists of those elements in exactly one of the sets. Use +uni:in with +dif:in to identify this set.
For instance, if A = {a, b, c} and B = {c, d, e}, then A Δ B = {a, b, d, e}.
Set Operations
Logical AND (∧)
AND (∧)+all:in computes the logical AND on every element in set A against a logical function f, producing a flag.
Logical OR (∨)
OR (∨)+any:in computes the logical OR on every element in set A against a logical function f, producing a flag.
Operate with Function
+run:in applies a function f to every member of set A.
Accumulate with Function
+rep:in applies a binary function f to every member of set A and accumulates the result.
While there are a few other set functions in +in, they are largely concerned with internal operations such as consistency checking.
Last updated