Arvo
Arvo, also called Urbit OS, is our operating system.
This article is intended to provide a thorough summary of all of the most important aspects of the Arvo kernel and how this functionality gives life to the ambitions of the Urbit platform.
We work on two levels:
A conceptual level that should be useful to anybody interested in what Urbit is.
A more technical level for those that intend to write software on Urbit.
The Urbit whitepaper is a good companion to this document; some segments of this page are direct quotes or paraphrases, but it should be noted that some parts of the whitepaper are now either out of date or not yet implemented. This 2024 article reflects on what's changed since the whitepaper.
Prerequisites
The conceptual section titled What is Arvo? can be understood without knowing Hoon, the Urbit programming language.
The kernel section will require having read the first page of Hoon School for full understanding, and some material from the second page will be helpful as well.
We also suggest to the reader to consult the glossary while reading this page.
What is Arvo?
Arvo is a new operating system built to run a new, peer-to-peer internet whereby users own and manage their own data.
Today, your life online is spread out across multiple services hosted on massive data centres. These are cost centers for the corporate web platforms that use them, centralized points of failure for the networks the modern world depends on, and an ideal position for foreign, domestic, state and non-state actors to monitor network traffic.
Urbit is an effort to replace this with one server, ideally in your own home, to contain all the apps and data you care about. It's not a platform, it's not a service, it's yours: you own your software, hardware, and identity completely. Every message between two Urbit servers is encrypted in transit, and shared just between them.
Every architectural decision in Arvo was made with this goal in mind.
Arvo won't replace Windows, macOS, or Linux anytime soon; for now it runs as a virtual machine on any macOS/Linux machine, but it could one day operate on bare metal built to run Nock.
Arvo is designed to avoid the usual state of complex event networks: event spaghetti. We keep track of every event's cause so that we have a clear causal chain for every computation. At the bottom of every chain is a Unix I/O event, such as a network request, terminal input, file sync, or timer event. We push every step in the path the request takes onto the chain until we get to the terminal cause of the computation. Then we use this causal stack to route results back to the caller.
Arvo is small enough for one person to understand completely. It's around 57,000 lines of code, and the kernel itself is only around 2,000 lines of code. You have used bigger websites. The difficulty in understanding, administering, and maintaining a codebase is roughly proportional to its size, which is why we want Arvo to be as small as possible.
An operating function
A "pure function" is a function that always produces the same output given the same input. Arvo is the first purely functional operating system, and as such it may reasonably be called an operating function. The importance of understanding this design choice and its relevance to the overarching goal cannot be understated.
This means two things:
There is a notion of "state" for the entire operating system.
The current state is a pure function of its event log: a chronological record of every action the operating system has ever performed.
This means Arvo is deterministic. Other operating systems are non-deterministic, for example because they allow programs to alter global variables that affect the operation of other programs.
In mathematical terms, one may think of Arvo as being given by a transition function T:
In practice, T is implemented by the +poke function in the Arvo kernel, which is described in more detail in the kernel section. In theoretical terms, it may be more practical to think of Arvo as being defined by a lifecycle function we denote here by L:
Which perspective is more fruitful depends on the problem being considered.
Determinism
We consider Arvo to be deterministic at a high level. By that we mean that it is stacked on top of a frozen instruction set known as Nock. Frozen instruction sets are a new idea for an operating system, but not for computing in general. For instance, the CPU instruction sets such as x86-64 are frozen at the level of the chip. A given operating system may be adapted to run on more than one CPU instruction set, we merely freeze the instruction set at a higher level in order to enable deterministic computation.
Arvo handles nondeterminism in an interesting way. Deciding whether or not to halt a computation that could potentially last forever becomes a heuristic decision that is akin to dropping a packet. Thus it behooves one to think of Arvo as being a stateful packet transceiver rather than an ordinary computer: events are never guaranteed to complete, even if one can prove that the computation would eventually terminate. We elaborate on this in the solid state interpreter section.
Because Arvo is run on a virtual machine, nondeterministic information such as the stack trace of an infinite loop that was entered into may be obtained. This is possible because while Arvo may be unable to obtain that information, the runtime may inject that information into the event log.
Being deterministic at a high level enables many things that are out of reach of any other operating system. For instance, we are able to do over-the-air (OTA) updates, which allows software updates to be implemented across the network without needing to worry whether it won't work on someone's ship. Since Arvo is an interpreter, it can accept source code with which to update itself instead of requiring a pre-compiled binary. This essential property makes Urbit much simpler and more accessible than any comparable personal server setup.
Event log
The formal state of an Arvo instance is an event history, as a linked list of nouns from first to last. The history starts with a bootstrap sequence that delivers Arvo itself, first as an inscrutable kernel written in Nock, then as the self-compiling Hoon source code for that kernel.
This is a special portion of the Arvo lifecycle known as the larval stage. We describe this in more detail in the larval stage section.
Once it's booted, an Arvo instance is made unique by identity (an Urbit ID) and entropy (some hashed data used for pseudo-random number generation). The rest of the event log thereafter is actual input.
In principle, this event log is maintained by the Urbit runtime, but in practice event logs become too long over time to keep, as the event log has a size of O(n) where n is the number of events. For that reason, the runtime can make periodic snapshots of the state of Arvo and delete the event log up until that state.
More information on the structure of the Arvo event log and state is given in the section on the kernel.
Solid state interpreter
Arvo is a solid state interpreter. In this section we describe what is meant by this new term, and how this behavior derives from the fact that Arvo is an ACID database and a single-level store.
In computer science, an interpreter is a program that directly executes instructions written in some human-understandable programming or scripting language, rather than requiring the code to first be compiled into a machine language.
Arvo is an interpreter, which is important for us since it allows us to perform deterministic over-the-air updates by the direct transfer of raw source code.
To understand what we mean by "solid state" interpreter, consider the operation of a solid state drive (SSD) when a computer shuts down or loses power.
Data written to an SSD is permanent unless it's specifically deleted: loss of power may leave some partially written data, but nothing is ever lost. Thus, the state of an SSD can be considered to be equivalent to the data that it contains. That is to say, you do not need to know anything about the system which is utilizing the SSD to know everything there is to know about the SSD. There is no notion of "rebooting" an SSD; it simply stores data, and when power is restored to it, it is in exactly the same state as it was when power was lost.
Contrast this with mainstream operating systems such as Windows, macOS, or Linux.
The state of the operating system is something that crucially depends on having a constant power supply because much of the state of the operating system is stored in RAM, which is volatile. When you reboot your computer or suddenly lose power, any information stored in RAM is lost. Modern operating systems do mitigate this loss of information to some extent. For instance, it may remember what applications you were running at the time power was lost and try to restore them. Particularly durable programs may go as far as writing their state to disk every few seconds so that only very minimal information can be lost in a power outage. However, this is not the default behavior, and indeed if it were then they would be so slow as to be unusable, as you would effectively be using your hard disk as the RAM.
How Arvo handles loss of power is closer to that of an SSD. Since it is an ACID database and a single-level store, a sudden loss of power has no effect on the state of the operating system. When you start your ship back up, it will be exactly as it was before the failure. Your information can never be lost, and because it was designed from the ground up to behave in this fashion, it does not suffer significant slowdown by persisting all data in this manner as would be the case if your typical operating system utilized its hard disk as RAM.
Another way to describe a solid state interpreter is to think of it as a stateful packet transceiver. Imagine it as a chip. Plug this chip into power and network; packets go in and out, sometimes changing its state. The chip never loses data and has no concept of a reboot; every packet is an ACID transaction.
Over-the-air updates
Arvo can hotpatch any other semantics at any layer in the system (apps, vanes, Arvo or Hoon itself) with automatic over-the-air updates.
Typically, updates to an operating system are given via a pre-compiled binary, which is why some updates will work on some systems but not on others where the hardware and environment may differ. This is not so on Arvo - because it is an interpreter, Arvo may update itself by receiving source code from your sponsor over the Urbit network. As Hoon compiles down to Nock, which is an axiomatic representation of a deterministic computer, this code is guaranteed to run identically on your machine as it would on anybody else's.
Some subtleties regarding types arise when handling OTA updates, since they can potentially alter the type system. Put more concretely, the structure of Hoon's $type type may be updated. In that case, the update is an untyped Nock formula from the perspective of the old kernel, but ordinary typed Hoon code from the perspective of the new kernel. Besides this one detail, the only functionality of the Arvo kernel proper that is untyped are its interactions with Unix.
ACID Database
In the client-server model of the internet, data is stored on the server and thus reliable and efficient databases are an integral part of server architecture. This is not quite so true for the client: a user may be expected to reboot their machine in the middle of a computation, alter or destroy their data, never make backups, never perform version control, etc. In other words, client systems like your personal computer or phone are not well suited to act as databases.
In order to dismantle the client-server model and build a peer-to-peer internet, we need to put a robust modern database server in the hands of the user. So Arvo itself must have all of the properties of a reliable database.
Database theory studies, in precise terms, the possible properties of anything that could be considered to be a database. In this context, Arvo has the properties of an ACID database, and the Ames network could be thought of as network of such databases. ACID stands for atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. We review here how Arvo satisfies these properties.
Atomicity: Events in Arvo are atomic, meaning that they either succeed completely or fail completely. In other words, there are no transient periods in which something like a power failure will leave the operating system in an invalid state. When an event occurs in Arvo, e.g. the kernel is
+poked, the effects of an event are computed, the event is persisted by writing it to the event log, and only then are the actual effects applied.Consistency: Every possible update to the database's state puts it into another valid state. Given that Arvo is purely functional, this is easier to accomplish than it would be in an imperative setting.
Isolation: Transactions in databases often happen concurrently, and isolation ensures that the transactions occur as if they were performed sequentially, making it so that their effects are isolated from one another. Arvo ensures this simply by the fact that it only ever performs events sequentially. While Arvo transactions are sequential and performed by the daemon, persistence and effect application are performed in parallel by the worker. (See worker and daemon for more detail.)
Durability: Completed transactions will survive permanently. In other words, since the event log is stored on disk, if power is lost you are guaranteed that no transactions will be reversed.
It is easy to think that "completed transaction will survive permanently" along with "the state of Arvo is pure function of its event log" implies that nothing can ever be deleted. This is not quite true.
Clay is our referentially transparency file system, which could naively be thought to mean that since data must be immutable, files cannot be deleted. However, Clay can replace a file with a "tombstone" that causes Clay to crash whenever it is accessed. Referential transparency only guarantees that there won't be new data at a previously accessed location, not that it will still be available.
Single-level store
A kernel which presents the abstraction of a single layer of permanent state is also called a single-level store.
One way to describe a single-level store is that it never reboots; a formal model of the system does not contain an operation which unpredictably erases half of its brain.
Today's operating systems utilize at least two types of memory: the hard disk and the RAM, and this split is responsible for the fact that data is lost whenever power is lost. Not every operating system in history was designed this way. In particular, Multics utilized only one store of memory. Arvo takes after Multics: all data is stored in one permanent location, and as a result no data is ever lost when power is lost.
Non-preemptive
Most operating systems are preemptive, meaning that they regularly interrupt tasks being performed with the intention of resuming that task at a later time, without the task explicitly yielding control. Arvo does not do this. Tasks run until they are complete or are cancelled due to some heuristic, such as taking too long or because the user pressed Ctrl+C. This is known as non-preemptive or cooperative multitasking.
Parts of the remainder of this document are out of date as of 2020.07.20, please use information here with caution. This message will be removed once it is up to date.
The kernel
The Arvo kernel, stored in sys/arvo.hoon, is about 1k lines of Hoon whose primary purpose is to implement the transition function, +poke. In this section we point out the most important parts of arvo.hoon and describe their role in the greater system. We also give brief descriptions of Arvo's kernel modules, known as vanes, and how Arvo interfaces with them.
This section requires an understanding of Hoon of at least the level of Chapter One of the Hoon tutorial.
After concluding this section, the reader is encouraged to follow along with the move trace tutorial, which applies many of the concepts covered below.
Overall structure
arvo.hoon contains five top level cores as well as a "formal interface" consisting of a single gate that implements the transition function. They are nested with the =< and => runes like so, where items lower on the list are contained within items higher on the list:
Types
Section 3bE Arvo Core
Implementation core
Structural interface core, or adult core
Larval stage core
Formal interface
See Hoon School “Subject-Oriented Programming” for further explanation of what is meant here by “nesting”. We now describe the functionality of each of these components.
Formal interface
The formal interface is a single gate that takes in the current time and a noun that encodes the input. This input, referred to as an event, is then put into action by the +poke arm, and a new noun denoting the current state of Arvo is returned. In reality, you cannot feed the gate just any noun - it will end up being an $ovum described below - but as this is the outermost interface of the kernel the types defined in the type core are not visible to the formal interface.
Types
This core contains the most basic types utilized in Arvo. We discuss a number of them here.
$duct
Arvo is designed to avoid the usual state of complex event networks: event spaghetti. We keep track of every event's cause so that we have a clear causal chain for every computation. At the bottom of every chain is a Unix I/O event, such as a network request, terminal input, file sync, or timer event. We push every step in the path the request takes onto the chain until we get to the terminal cause of the computation. Then we use this causal stack to route results back to the caller.
The Arvo causal stack is called a $duct. This is represented simply as a list of paths, where each path represents a step in the causal chain. The first element in the path is the first letter of whichever vane handled that step in the computation, or the empty path element for Unix.
Here's a $duct that was recently observed in the wild upon entering -time ~s1 into the dojo and pressing Enter, which sets a timer for one second that will then produce a @d with the current time after the timer has elapsed:
This is the $duct that the timer vane, Behn, receives when the $time sample app asks the Behn to set a timer. This is also the $duct over which the response is produced at the specified time. Unix sent a terminal keystroke event (Enter), and Arvo routed it to Dill (our terminal), which passed it on to the Gall app terminal, which sent it to shell, its child, which created a new child (with process id 4), which on startup asked Behn to set a timer.
Behn saves this $duct, so that when the specified time arrives and Unix sends a wakeup event to the timer vane, it can produce the response on the same $duct. This response is routed to the place we popped off the top of the $duct, i.e. the time app. This app returns a @d which denotes the current time, which falls down to the shell, which drops it through to the terminal. Terminal drops this down to Dill, which converts it into an effect that Unix will recognize as a request to print the current time to the screen. When Dill produces this, the last path in the $duct has an initial empty element, so this is routed to Unix, which applies the effects.
This is a call stack, with a crucial feature: the stack is a first-class citizen. You can respond over a $duct zero, one, or many times. You can save $ducts for later use. There are definitely parallels to Scheme-style continuations, but simpler and with more structure.
$wire
Synonym for $path, used in $ducts. These should be thought of as a list of symbols representing a cause.
$move
If $ducts are a call stack, then how do we make calls and produce results? Arvo processes $moves which are a combination of message data and metadata. There are four types of $moves: %pass, %give, %slip, and %unix.
A %pass $move is analogous to a call:
Arvo pushes the return path (preceded by the first letter of the vane name) onto the $duct and sends the given data, a $card, to the vane we specified. Any response will come along the same $duct with the $wire return-path.
A %give $move is analogous to a return:
Arvo pops the top $wire off the $duct and sends the given $card back to the caller.
A %slip $move is a cousin of %pass. Any $card that can be %passed can also be %slipped, but while a %pass says to "push this $wire onto the $duct and transfer control to the receiving vane", a %slip transfers control to the receiving vane without altering the $duct. Therefore, a %give in response to a %slip will go to the caller of the vane that sent the %slip rather than the vane that actually sent the %slip. %slips are much more rare than %passes and %gives. In general, %slip and %pass $moves are both referred to as "passes" and it should be clear from the context if one means to refer only to %passes and not %slips or vice versa. Lastly, we note that %slip is a code smell and should nearly always be avoided. It can result in unexpected behavior like receiving a gift from a vane you never passed a note to.
Lastly, a %unix $move is how Arvo represents communication from Unix, such as a network request or terminal input.
$cards and curds
$cards are the vane-specific portion of a $move, while curds are typeless $cards utilized at the level of the kernel. $cards are not actually defined in arvo.hoon, rather they are given by +note-arvo and +sign-arvo in the standard library zuse (which then refer to +task and +gift in each of the vane cores), but they are closely connected to curds so we speak of them in the same breath.
Each vane defines a protocol for interacting with other vanes (via Arvo) by defining four types of $cards: tasks, gifts, $notes, and $signs.
When one vane is %passed a $card in its task (defined in zuse), Arvo activates the +call gate with the $card as its argument. To produce a result, the vane %gives one of the $cards defined in its gift. If the vane needs to request something of another vane, it %passes it a $note $card. When that other vane returns a result, Arvo activates the +take gate of the initial vane with one of the $cards defined in its $sign.
In other words, there are only four ways of seeing a $move: (1) as a request seen by the caller, which is a $note. (2) that same request as seen by the callee, a task. (3) the response to that first request as seen by the callee, a gift. (4) the response to the first request as seen by the caller, a $sign.
When a task $card is %passed to a vane, Arvo calls its +call gate, passing it both the $card and its $duct. This gate must be defined in every vane. It produces two things in the following order: a list of $moves and a possibly modified copy of its context. The $moves are used to interact with other vanes, while the new context allows the vane to save its state. The next time Arvo activates the vane it will have this context as its subject.
This cycle of %passing a $note to %passing a task to %giveing a gift to %giveing a %sign is summarized in the following diagram:
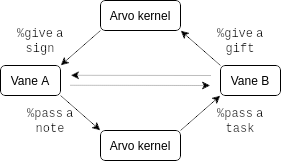
Note that %passing a $note doesn't always result in a return - this diagram just shows the complete cycle. However, %giveing a gift is always in response to being %passed some task. Since the Arvo kernel acts as a middleman between all $moves in Arvo, in diagrams we will generally represent the intermediate steps of a vane %passing a $note to the kernel addressed to another vane followed by the kernel %passing a task to the addressed vane as a single arrow from one vane to the other to make the diagrams less cluttered.
This overview has detailed how to pass a $card to a particular vane. To see the $cards each vane can be %passed as a task or return as a gift (as well as the semantics tied to them), each vane's public interface is explained in detail in its respective overview.
$ovum
This mold is used to represent both steps and actions.
A pair of a $wire and a curd, with a curd being like a typeless $card. The reason for a typeless $card is that this is the data structure which Arvo uses to communicate with the runtime, and Unix events have no type. Additionally, upgrading the kernel may alter the type system and thus may not be able to be described within the current type system. Then the $wire here is the default Unix $wire, namely //. In particular, it is not a $duct because $ovums come from the runtime rather than from within Arvo.
Arvo cores
arvo.hoon has four additional cores that encode the functionality of Arvo. The larval core, structural interface core, and implementation core each have five arms, called +come, +load, +peek, +poke, and +wish. Of these five arms, only +poke affects the Arvo state, while the rest leave the state invariant. Thus +poke is the aforementioned transition function that sends Arvo from one state to the next.
A short summary of the purpose of each these arms are as follows:
+pokeis the transition function that$moves Arvo from one state to the next. It is the most fundamental arm in the entire system. It is a typed transactional message that is processed at most once. If the+pokecauses Arvo to send an message over Ames Ames guarantees that the message will be delivered exactly once. This is sometimes said to be impossible, and it is for standard operating systems, but that is not the case for single-level stores engaged in a permanent session, as is the case among Arvo ships.+peekis an arm used for inspecting things outside of the kernel. It grants read-only access to+scryArvo's global referentially transparent namespace. It takes in a$pathand returns aunit (unit). If the product is~, the path is unknown and its value cannot be produced synchronously. If its product is[~ ~]the$pathis known to be unbound and can never become bound. Otherwise the product is a$markand a noun.+wishis a function that takes in a core and then parses and compiles it with the standard library,zuse. It is useful from the outside if you ever want to run code within. One particular way in which it is used is by the runtime to read out the version ofzuseso that it knows if it is compatible with this particular version of the kernel.+loadis used when upgrading the kernel. It is only ever called by Arvo itself, never by the runtime. If upgrading to a kernel where types are compatible,+loadis used, otherwise+comeis used.+comeis used when the new kernel has incompatible types, but ultimately reduces to a series of+loadcalls.
The Section 3bE core does not follow this pattern.
Section 3bE core
This core defines helper functions that are called in the larval and adult cores. These helper functions are placed here for safety so that they do not have access to the entire state of Arvo, which is contained in the structural interface core. One reason this core is required is that the Arvo interface has only five arms and additional arms are required to perform everything the kernel needs to do in a clean manner, so they must be segregated from the other three cores that stick to the five-arm paradigm.
Implementation core
This core is where the real legwork of the Arvo kernel is performed during the adult stage. It does not communicate with Unix directly, rather it is called by the structural interface core.
Structural interface core
This core could be thought of as the primary "adult core" - the one that is in operation for the majority of its lifecycle and the one that contains the Arvo state. This core should be thought of as an interface - that is, the amount of work the code does here is minimal as its main purpose is to be the core that communicates with Unix, and Unix should not be able to access deeper functions stored in the implementation core and 3bE core on its own. Thus, arms in this core are there primarily to call arms in the implementation core and 3bE core.
Larval stage core
This core is in use only during the larval stage of Arvo, which is after the Arvo kernel has compiled itself but before it has "broken symmetry" by acquiring identity and entropy, the point at which the larval stage has concluded. We call this breaking symmetry because prior to this point, every Urbit is completely identical. The larval stage performs the following steps in order:
The standard library,
zuse, is installed.Entropy is added
Identity is added
Metamorph into the next stage of Arvo
Once the larval stage has passed its functionality will never be used again.
The state
As we follow functional programming paradigms, the state of Arvo is considered to be the entire Arvo kernel core currently in operation (whether it be the larval stage or adult stage). Thus when +poke is performed, a new core with the updated state is produced, rather than modifying the existing core as would be expected to happen in an imperative setting.
Thus besides the battery of the Arvo core, we have the payload which is as follows.
Let's investigate the state piece by piece.
This $vase is part of the state but does not get directly migrated when +poke is called. !>(..is) consists of the code in arvo.hoon written above this core contained in a $vase. Thus this part of the state changes only when that code changes in an update.
This is a cache of specific types that are of fundamental importance to Arvo - namely $types, $ducts, $paths, and $vases. This is kept because it is unnecessarily wasteful to recompile these fundamental types on a regular basis. Again, this part of the state is never updated directly by +poke.
This is where the real state of the Arvo kernel is kept. lac detemines whether Arvo's output is verbose, which can be set using the |verb command in the dojo. eny is the current entropy. our is the ship, which is permanently frozen during the larval stage. bud is the standard library. Lastly, vanes is of course the list of vanes, which have their own internal states.
As you can see, the state of Arvo itself is quite simple. Its primary role is that of a traffic cop, and most of the interesting part of the state lies in vanes.
Vanes
The Arvo kernel can do very little on its own. Its functionality is extended in a careful and controlled way with vanes, also known as kernel modules.
As described above, we use Arvo proper to route and control the flow of $moves. However, Arvo proper is rarely directly responsible for processing the event data that directly causes the desired outcome of a $move. This event data is contained within a $card. Instead, Arvo proper passes the $card off to one of its vanes, which each present an interface to clients for a particular well-defined, stable, and general-purpose piece of functionality.
As of this writing, we have nine vanes, which each provide the following services:
Ames: the name of both our network and the vane that communicates over it.
Behn: a simple timer.
Clay: our version-controlled, referentially- transparent, and global filesystem.
Dill: a terminal driver. Unix sends keyboard events to
%dillfrom the console, and%dillproduces terminal output.Eyre: an http server. Unix sends http messages to
%eyre, and%eyreproduces http messages in response.Gall: manages our userspace applications.
%gallkeeps state and manages subscribers.Iris: an http client.
Jael: storage for Azimuth information.
Khan: control plane and thread runner.
Applying your knowledge
Now that you've learned about the nuts and bolts of the Arvo kernel, why not check it out in action? An in-depth "move trace" tutorial for running a timer app is available here.
Last updated