Fundamentals
Introduction
A thread is like a transient gall agent. Unlike an agent, it can end and it can fail. The primary uses for threads are:
Complex IO, like making a bunch of external API calls where each call depends on the last. Doing this in an agent significantly increases its complexity and the risk of a mishandled intermediary state corrupting permanent state. If you spin the IO out into a thread, your agent only has to make one call to the thread and receive one response.
Testing - threads are very useful for writing complex tests for your agents.
Threads are managed by the Gall agent called %spider. You can poke %spider directly, or you can pass a task to the Khan thread runner vane and let it handle %spider for you.
Threads can be run from a file in the /ted directory, or an "inline thread" can be passed directly to Khan from within your agent.
Thread file location
Thread files live in the /ted directory of each desk. For example, in a desk named %sandbox:
%sandbox
├──app
├──gen
├──lib
├──mar
├──sur
└──ted <-
├──foo
│ └──bar.hoon
└──baz.hoonFrom the dojo, ted/baz.hoon can be run with -sandbox!baz, and ted/foo/bar.hoon with -sandbox!foo-bar. Threads in the %base desk can just be run like -foo, but all others must have the format -desk!thread.
Libraries
There are two libraries that may be relevant:
/sur/spider/hoon- this contains a few simple structures used by%spider. It's only relevant if you're running thread files by poking%spiderdirectly. If you're running them by passing a task to Khan as is typical, it can be ignored./lib/strandio/hoon- this contains a large collection of ready-made functions for use in threads. You'll likely use many of these when you write threads, so it's very useful.
Thread definition
A thread is defined as a $-(vase shed:khan). That is, a gate that takes a $vase and produces a $shed:khan. A $shed:khan is the +form of a strand that produces a $vase. This is a little confusing and we'll look at each part in detail later. For now, note that the thread doesn't just produce a result, it actually produces a strand that takes input and produces output from which a result can be extracted. It works something like this:
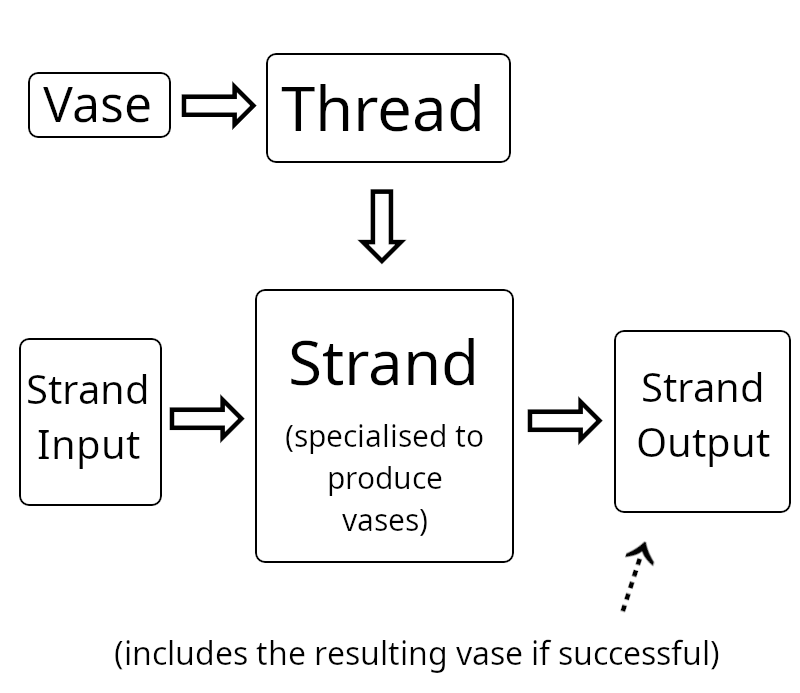
This is because threads typically do a bunch of I/O so it can't just immediately produce a result and end. Instead the strand will get some input, produce output, get some new input, produce new output, and so forth, until they eventually produce a %done with the actual final result.
Strands
Strands are the building blocks of threads. A thread will typically compose multiple strands.
A strand is a function of $strand-input:rand to $output:strand:rand, the latter of which is a +strand-output-raw:rand initialized with a particular mold:
At this stage you don't need to know the nitty-gritty details but it's helpful to have a quick look through the +rand arm in lull.hoon. We'll discuss these things in more detail later.
A strand is a core that has three important arms:
+form- the mold of the strand+pure- produces a strand that does nothing except return a value+bind- monadic bind, likethenin javascript promises
We'll discuss each of these arms later.
A strand must be specialised to produce a particular type like (strand:rand ,<type>). As previously mentioned, a thread produces a $vase so is specialised like (strand:rand ,vase). Within your thread you'll likely compose multiple strands which produce different types like (strand:rand ,@ud), (strand:rand ,[path cage]), etc, but the thread itself will always come back to a (strand:rand ,vase).
Strands are conventionally given the face m like:
NOTE: a comma prefix as in ,vase is the irregular form of ^: ketcol which produces a gate that returns the sample value if it's of the correct type, but crashes otherwise.
Form and Pure
+form
+formThe +form arm is the mold of the strand, suitable for casting. The two other arms produce +forms so you'll cast everything to this like:
+pure
+purePure produces a strand that does nothing except return a value. So, (pure:(strand:rand ,@tas) %foo) is a strand that produces %foo without doing any IO.
We'll cover +bind later.
A trivial thread
The above code is a simple thread that just returns its argument, and it's a good boilerplate to start from.
Save the above code as a file in ted/mythread.hoon and |commit it. Run it with -mythread 'foo', you should see the following:
NOTE: The dojo wraps arguments in a unit so that's why it's [~ 'foo'] rather than just 'foo'.
Analysis
We'll go through it line-by line.
We create a gate that takes a vase, the first part of the previously mentioned thread definition.
Inside the gate we create our +strand specialised to produce a $vase and give it the canonical face m.
We cast the output to +form - the mold of the strand we created.
Finally we call +pure with the gate input arg as its argument. Since arg is a $vase it will return the +form of a +strand which produces a $vase. Thus we've created a thread in accordance with its type definition.
Inline Threads
While you can store threads as files in the /ted directory, you can also include threads directly in your Gall agent code and ask the Khan vane to run them.
While a stand-alone thread file is expected to be a $-(vase shed:khan), an inline thread is just a $shed:khan. That is, it doesn't take any initial argument argument. Instead, you can simply reference any data and functions available in its subject in the Gall agent.
Here's how a trivial inline thread that'll just return 123, a number pinned previously in the Gall agent, might look:
The $shed can then be passed to Kahn in card:
The result will come back into the +on-arvo arm of the Gall agent in an %arow gift.
Next we'll look at the third arm of a strand: +bind.
Last updated